Understanding MST and SST Modes: Unlocking the Full Potential of DisplayPort Technology
As multi-monitor workstations and high-performance productivity setups become the norm, understanding the difference between MST (Multi-Stream Transport) and SST (Single-Stream Transport) becomes critical for both Windows and macOS users. At wfyear, we’ve created a clear visual guide to help you grasp the key concepts and functionalities of these two protocols.
What is MST Mode?
Multi-Stream Transport (MST) is a powerful feature supported by DisplayPort 1.2 and above. It enables a single host device—such as a desktop or laptop—to transmit video signals to multiple independent displays through one single DisplayPort output. MST mode fully unleashes its potential on Windows platforms, especially when used with compatible MST hubs or daisy-chain-ready monitors.
MST Key Features:
Supports Extended Mode: each screen acts independently with separate resolution and orientation.
Enables Mirror Mode: all displays duplicate the primary screen.
Uses MST hubs or daisy-chaining to connect multiple monitors.
Ideal for advanced multitasking, creative workflows, and enterprise setups.
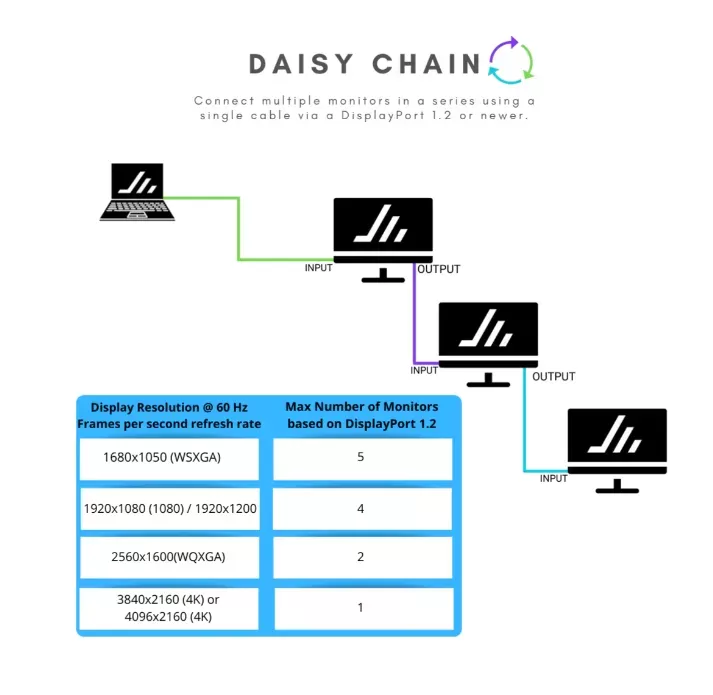
What is Daisy-Chaining?
Daisy-chaining is the practice of connecting monitors in series, allowing multiple displays to run from a single DisplayPort connection. With DisplayPort 1.2’s in/out support, this setup drastically reduces cable clutter and enhances display scalability.
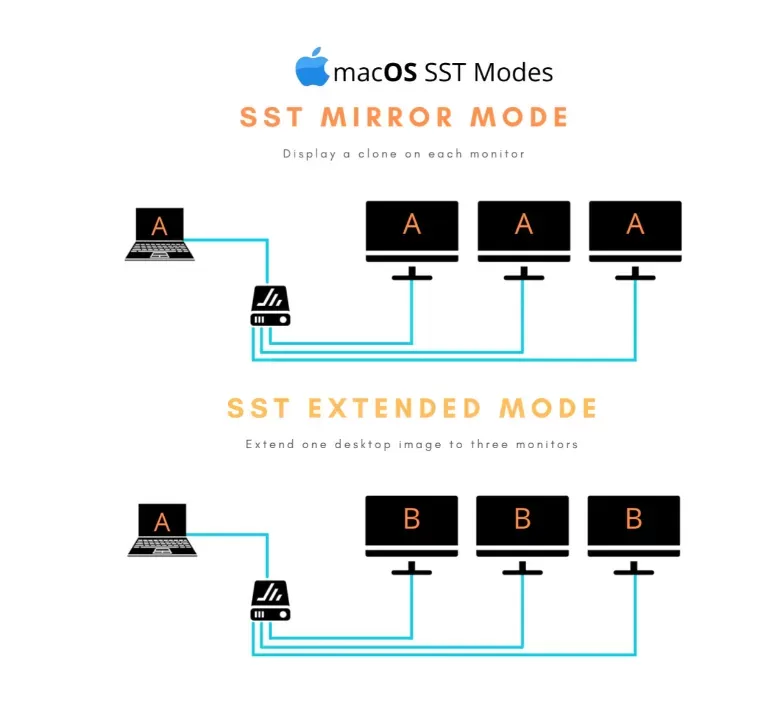
What is SST Mode?
Single-Stream Transport (SST), also based on DisplayPort, supports only one display per port at a time. However, it can extend or mirror content onto a second screen. On macOS, SST is the primary supported mode.
SST Highlights:
Common in macOS ecosystems.
Suitable for basic dual-screen setups.
Doesn’t support daisy-chaining or MST features.
At wfyear, we aim to provide professional-grade DisplayPort solutions for every kind of setup—whether you're using Thunderbolt 4, USB-C with DP Alt Mode, or MST docking stations. Check out our latest MST-compatible docking solutions to elevate your workflow.
Suggested Images
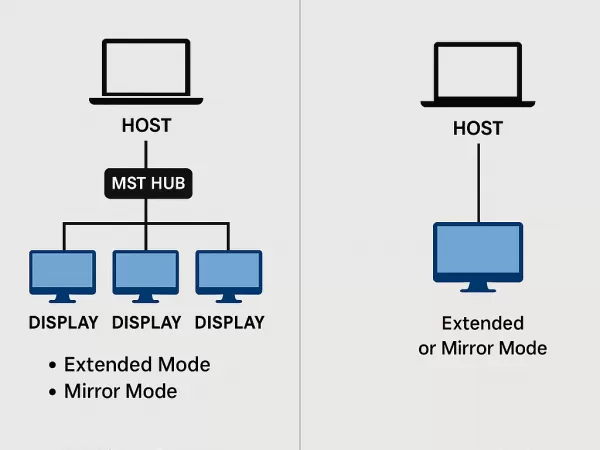
Image 1: MST vs SST Comparison Diagram
Side-by-side graphic showing:
MST: One host → MST hub → Multiple displays (extended/mirrored)
SST: One host → One display
Image 2: MST Daisy-Chaining Flow
A diagram showing:
Host → Monitor 1 → Monitor 2 → Monitor 3 (with DisplayPort pass-through)
Image 3: Platform Compatibility Table
Table comparing MST and SST:
Feature MST (Windows) SST (macOS) Extended Display ✅ Multiple Displays ✅ Up to 2 Displays Daisy-Chaining ✅ Supported ❌ Not Supported Mirror Mode ✅ Supported ✅ Supported